Localization is a critically essential and crucial enabler of autonomous robots. While deep learning has made significant strides in many computer vision tasks, it is still yet to make a sizeable impact on improving capabilities of metric visual localization. One of the major hindrances has been the inability of existing CNN-based pose regression methods to generalize to previously unseen places. Our recently introduced CMRNet effectively addresses this limitation by enabling map independent monocular localization in LiDAR-maps.
CMRNet++ Demo
This demo contains localization examples on KITTI, Argoverse, and Lyft Level 5 datasets. Select a dataset to load from the drop down box below. CMRNet++ is trained on both KITTI and Argoverse datasets. All examples depict places that were never seen during the training phase. Note that the Lyft5 dataset was not included in the training set. We evaluate the generalization ability of CMRNet++ on Lyft5 without any retraining. Please see the Abstract section below for more details.
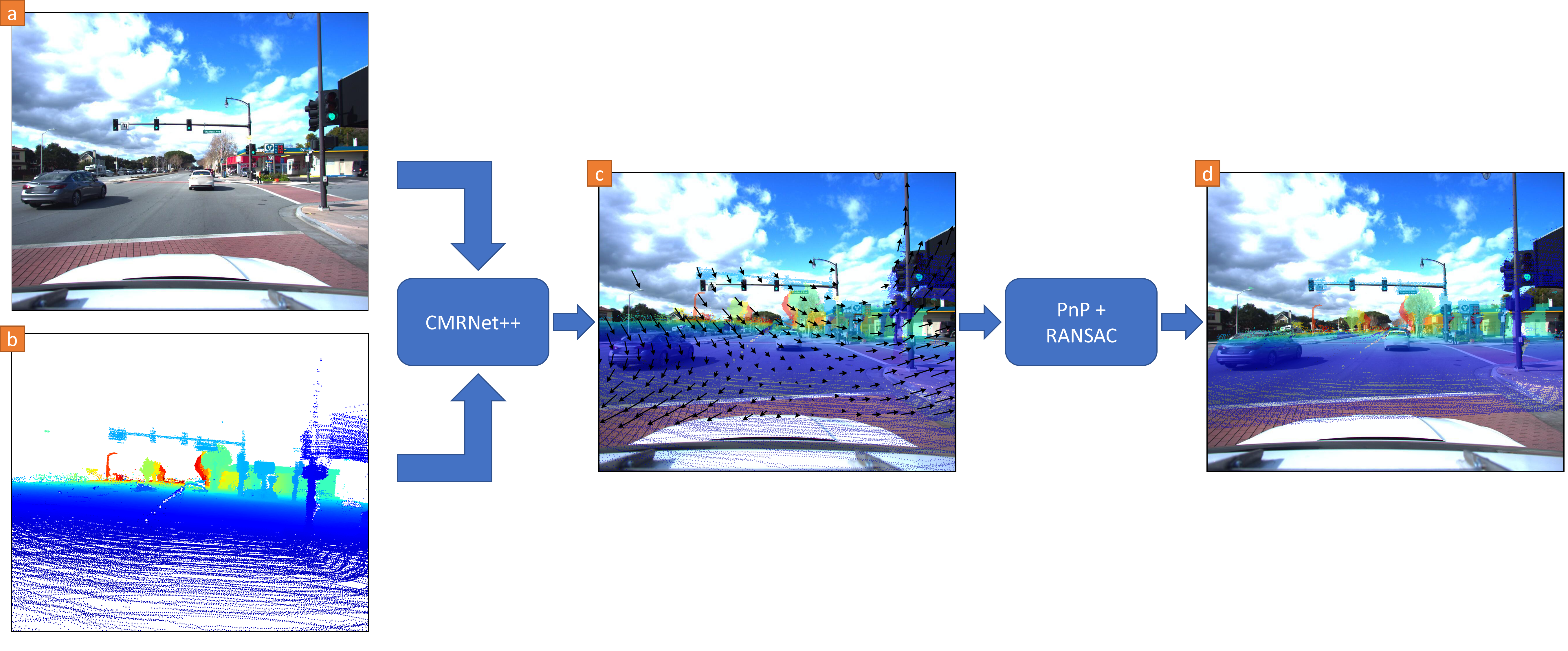
Given a pre-existing LiDAR map (for example, an HD map from map providers), a single RGB image, and a rough initial position estimate (e.g., obtained from GPS), we project the map's points on a virtual image plane placed at this initial position. If we overlay the resulting depth image on the RGB image, the two points of view strongly differ when the initial position is inaccurate. Click on any image to see the map projected from the position estimated by our CMRNet++. Our approach can effectively localize a single RGB image in any environment for which a LiDAR map is available, without any retraining or fine-tuning.
Please Select a Dataset:
Selected Dataset:
KITTI